15 of the Most Famous Sea Dinosaurs
When you hear the term “dinosaur,” towering giants like Tyrannosaurus or gentle herbivores like Brachiosaurus most likely spring to mind. Yet, a realm of these huge and impressive animals lived not on land, but beneath the waves, ruling the prehistoric oceans.

This article will explore the fascinating world of sea dinosaurs and marine reptiles and show you how as big as they were they were something entirely different to those huge land dinosaurs we all know and love.
What Actually is a Sea Dinosaur?
Many of the creatures popularly called “sea dinosaurs” are, in fact, not sea dinosaurs at all, they are not even dinosaurs. True dinosaurs were primarily land-dwelling, and their adaptation for life on land is one of the differences between them and other reptiles.
The majority of the creatures we commonly think of as “sea dinosaurs” are marine reptiles.
For instance, Ichthyosaurs and Plesiosaurs lived during the age of dinosaurs but weren’t sea dinosaurs themselves. They were marine reptiles, adapted explicitly for life in water.
Dinosaurs like Spinosaurus, on the other hand, were true dinosaurs that might have ventured into water but could not be described as sea dinosaurs.
Remember, while they’re commonly referred to as “sea dinosaurs,” technically these creatures are marine reptiles.

Evolution of Marine Reptiles
When one thinks of the term “sea dinosaurs” or “dinosaurs in the sea”, they’re often referring to a wide range of marine reptiles that ruled the oceans during the Mesozoic Era.
Around 250 million years ago, at the start of the Triassic Period, marine reptiles began to make their mark in the oceans.
This was shortly after the Permian-Triassic extinction event, which wiped out about 90% of all marine species.
The empty niches left by this catastrophic event provided an opportunity for reptiles to venture into the seas and evolve in the animals we call sea dinosaurs today.
Ichthyosaurs, resembling modern-day dolphins, were among the first to evolve. Their streamlined bodies and fin-like limbs made them adept swimmers and predators.
Following closely were the Plesiosaurs, with their long necks and broad bodies, and the Nothosaurs, which were likely coastal or lagoon inhabitants, and probably the closest to actually being sea dinosaurs without being dinosaurs.
During the Late Jurassic, Pliosaurs, a subgroup of the plesiosaurs, became the apex predators of the ocean. They had massive heads, sharp teeth, and powerful flippers.
The Late Cretaceous period saw the rise of Mosasaurs, giant sea-going lizards that dominated the marine food chain and some of the largest of these “sea dinosaurs.”
Apart from these primary groups, other marine reptiles like Thalattosaurs and the semi-aquatic Crocodylomorphs also played roles in the marine ecosystems of 250 to 66 million years ago.
While these marine reptiles lived in the seas for millions of years, the end of the Cretaceous brought about a mass extinction, wiping them out.
Today, the fossilized remains of these “sea dinosaurs” provides valuable insights into life in the prehistoric oceans.
The Groups of Sea Dinosaurs
It’s a common thought that all prehistoric creatures in the oceans were sea dinosaurs or marine dinosaurs. In truth, these sea-living giants belong to separate primary groups of marine reptiles,
we have some examples in the table below.
Table: Sea Dinosaur Groups and Examples.
| Sea Dinosaur Group | Examples |
| Ichthyosaurs | Ichthyosaurus, Stenopterygius, Temnodontosaurus |
| Plesiosaurs | Plesiosaurus, Elasmosaurus, Cryptoclidus |
| Mosasaurs | Mosasaurus, Tylosaurus, Platecarpus |
| Thalattosaurs | Askeptosaurus, Endennasaurus, Thalattosaurus |
| Pliosaurs | Liopleurodon, Kronosaurus, Pliosaurus |
| Choristoderes | Champsosaurus, Lazarussuchus, Cteniogenys |
| Crocodylomorphs | Dakosaurus, Metriorhynchus, Teleosaurus |
POP QUIZ: We have our list of 15 Sea dinosaurs below, but in fact only 2 are actually real dinosaurs, the others are marine reptiles, see if you can spot which ones and leave us a comment at the end if you can!
15 Of The Most Famous Sea Dinosaurs
Ichthyosaurus

One of the most famous dinosaurs of the sea, the Ichthyosaurus resembled today’s dolphins both in appearance, although they could be much bigger, and possibly in behavior.
Measuring up to 20 feet in length, these marine predators swam the oceans, like dinosaurs of the sea, during the Early Jurassic period, about 200 million years ago.
Found predominantly in what is now Europe, their sleek, streamlined bodies and large eyes suggest they were great hunters, preying on fish and squid.
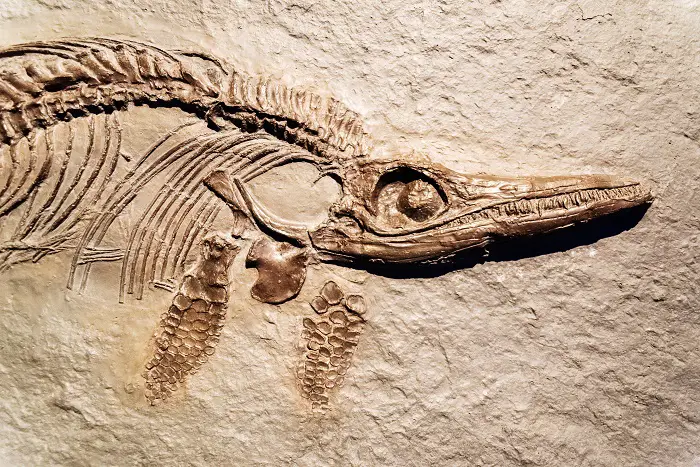

Their strong, paddle-like limbs allowed them to move quickly in water, making them one of the top predators of their time. Although they looked like dolphins you can see why people may think of them as sea dinosaurs.
Plesiosaurus
The Plesiosaurus, one of the most famous seas dinosaurs, had a long neck and four flippers which it used to glide gracefully beneath the waves.
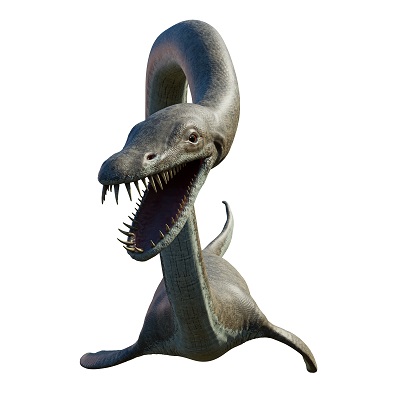

These creatures lived during the Early Jurassic period around 200 million years ago and were found in regions of Europe and parts of the Southern Hemisphere.
Ranging in size from 10 all the way up to 50 feet, their diet mainly consisted of fish and small marine animals.

With its long neck, the Plesiosaurus could strike swiftly, snatching prey from a distance without moving its body, a sneaky advantage in the marine world, and with the legend of Loch Ness including a plesiosaur it certainly is famous.
Mosasaurus

The Mosasaurus, a giant sea dinosaur, ruled the Late Cretaceous seas about 70 to 66 million years ago. Mainly discovered in regions of Europe and North America, they were the apex predators of their time.
With lengths reaching up to 50 feet, these behemoths dined on fish and other marine reptiles, and perhaps dinosaurs in the sea by accident or design.
Prehistoric Planet even shows one catching and eating a T-Rex juvenile while swimming in the ocean – we are not suggesting the T-Rex was a often in the sea just to be clear!
Their strong jaws, packed with razor-sharp teeth, and their muscular bodies made them the dominant force in ancient oceans and they were fast as well.
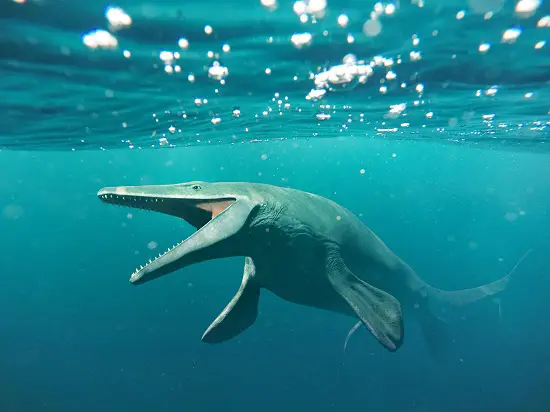

The Mosasaurus has gained recent popularity due to its impressive portrayal in Jurassic World movies, further cementing its status as one of the most famous and ferocious of the sea dinosaurs.
Kronosaurus

The mighty Kronosaurus was a true dinosaur of the sea, known for its ferociousness and enormous size.
Existing during the Early Cretaceous period, roughly around 125 to 100 million years ago, their fossils have been primarily uncovered in Australia and South America.

This sea dinosaur could grow to a remarkable 30 to 33 feet in length. Possessing a massive head and an mouth full of sharp, conical teeth, it ate mainly turtles, squids, and smaller marine reptiles.
Its name comes from the Greek titan Kronos.
Shastasaurus

Shastasaurus, a member of the ichthyosaur group, is a unique testament to the variety of dinosaurs in the sea. Predominantly found in Late Triassic deposits of North America, it existed around 210 to 205 million years ago.
Shastasaurus, the largest-known marine reptile, could span a staggering 69 feet in length and possibly more.
Contrary to the smaller and more popular ichthyosaurs, this marine dinosaur had a slender body and a reduced, toothless snout.

It’s believed that Shastasaurus would eat soft-bodied animals like cephalopods, using suction to catch its food.
Hesperornis

Hesperornis offers a rare glimpse into bird-like dinosaurs in the sea. Flourishing in the Late Cretaceous, about 83 to 78 million years ago, its fossils are primarily found in North America.
This bird reached lengths of up to 6 feet, and while its wings were tiny and probably useless for flight, its legs were robust and adapted for swimming.

With a long beak filled with sharp teeth, Hesperornis was an adept fish hunter, diving into the depths and capturing its prey with precision. it also makes an appearance in Prehistoric Planet 2 when pursed by a hungry Xiphactinus
Spinosaurus

Spinosaurus, a theropod dinosaur, may well have led its life as one of the group of dinosaurs in water. Although the vast majority of dinosaurs lived on land there were some, like Spinosaurus, that may have lived a semi aquatic lifestyle.
Existing around 112 to 93 million years ago in the Cretaceous, its remains are spread across North Africa.
Often called. if not the biggest than at least, the longest known carnivorous dinosaur, it could exceed 59 feet in length.

Unique for its sail-like structure on its back, recent evidence suggests Spinosaurus led a semi-aquatic life, hunting fish with its long, crocodile-like snout and conical teeth.
Though it would not have been a sea dinosaur, it maybe able to be classed as at least a river, lake or water dinosaur.
Its adaptations, such as dense bones and flat claws, further support the idea that it spent a significant portion of its life in water.
Shonisaurus

A true giant among the sea dinosaurs, the Shonisaurus stands out due to its impressive size. Living in the Late Triassic seas around 215 to 210 million years ago, their fossils have been chiefly found in North America.
With a length that could exceed 50 feet, it was among the largest of the ichthyosaurs.

Unlike its other ichthyosaur relatives, the Shonisaurus had a relatively toothless mouth but possessed a beak, indicating a diet that possibly included squid and other soft-bodied marine animals.
Its size alone would have made it a formidable presence in the ancient seas.
Tylosaurus
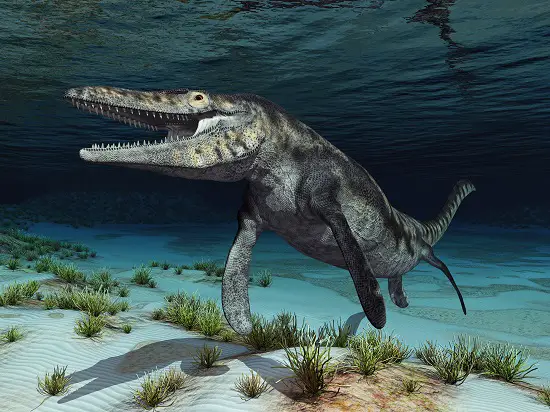

One of the apex predators among sea dinosaurs, Tylosaurus is a marine reptile that swam the oceans during the Late Cretaceous, about 85 to 80 million years ago.
Primarily unearthed in North America, these behemoths could grow up to 45 feet in length. Tylosaurus, a type of mosasaur, had a long, slender body, fin-like limbs, and an elongated, powerful jaw filled with sharp teeth.
This fearsome carnivore consumed a variety of prey, from fish to smaller marine reptiles.

Its name, derived from the Greek word ‘tylos’ meaning ‘knob’, refers to the snout’s unique rounded shape.
Liopleurodon
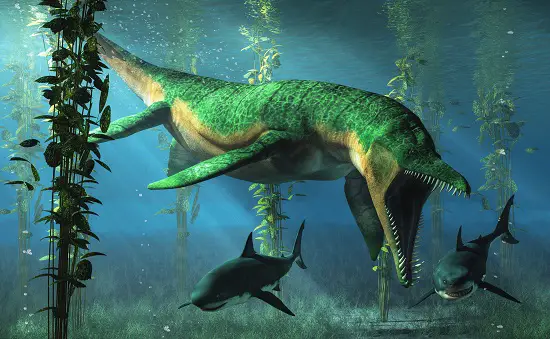
The Liopleurodon was a sea dinosaur, known for its size and incredible hunting prowess. Even being shown taking dinosaurs from land to eat. {we are not sure this happened though! ) it is not thought to be as big was the video below shows! which had it as 85 feet long!
Dominating the Middle to Late Jurassic seas, specifically around 160 to 155 million years ago, these predators had a vast range, with fossils discovered from Europe to parts of Asia.
Measuring up to 30 feet in length, they had four powerful, paddle-like limbs aiding their aquatic movement.
Their most remarkable feature was their huge jaws and sharp teeth, indicating a diet rich in fish and other marine reptiles.

Recent studies suggest that their sense of smell was highly developed, allowing them to track prey from great distances.
Elasmosaurus

One of the most iconic long-necked sea dinosaurs, the Elasmosaurus is often what comes to mind when we think of sea monsters of the stories.
Roaming the Late Cretaceous oceans around 80 million years ago, they were mainly found in North America. With a staggering length of nearly 34 feet, almost half of it was just their neck!
This unique feature allowed them to catch prey from afar without moving much of their body. Fish and squid formed the main bulk of their diet.

Their long, snake-like necks and small heads gave them a distinctive appearance that continues to fascinate marine paleontologists.
Nothosaurus

The Nothosaurus, has featured in quite a list of recent movies as a sea dinosaur. Including most recently the Meg 2: The Trench and as one of the dinosaurs from the sea in “65”.
It swam the Triassic waters around 240 to 210 million years ago.
It has mainly been found in Europe and China, these reptiles were medium-sized, generally spanning lengths of 13 feet.
Unlike most other other sea dinosaurs, Nothosaurus displayed features suited for both land and sea. With webbed feet and sharp teeth, their diet was diverse, including fish and other smaller marine creatures.
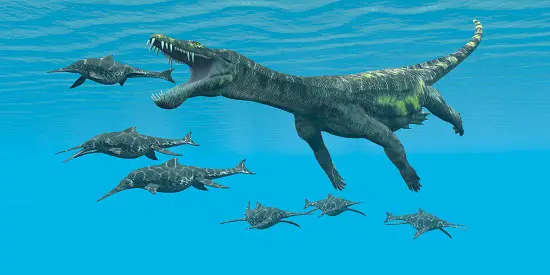
Their semi-aquatic nature suggests they might have ventured onto land occasionally, perhaps for laying eggs or basking, painting a picture of a versatile creature well-adapted to its environment.
Archelon

Archelon, while technically not a dinosaur of the sea, holds a special place in discussions about prehistoric marine life.
It lived in the Late Cretaceous period around 75 million years ago, its fossils have been predominantly found in the U.S., particularly South Dakota.
With a length reaching up to 13 feet, Archelon is the largest-known marine turtle. Unlike modern turtles, its shell wasn’t solid but rather a framework of bony plates beneath a leathery skin.

This magnificent creature likely munched on soft-bodied prey like squid, or jelly fish like modern turtle cousins.
Thalassomedon
Thalassomedon, translating to “sea lord”, . Inhabited the waters during the Late Cretaceous, around 95 million years ago, its primary fossils have been discovered in North America. if not a sea dinosaur it certainly looked like a sea monster.
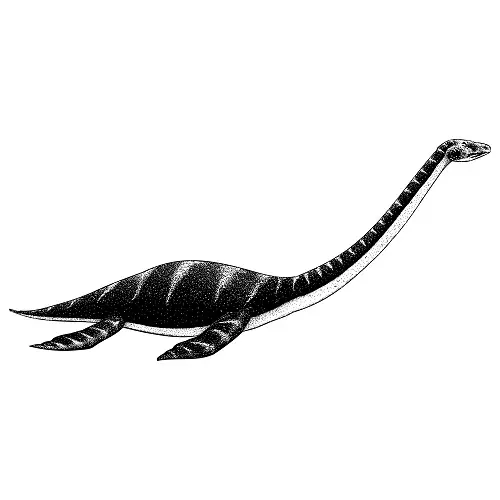

This plesiosaur, characterized by its remarkably long neck, could span up to 40 feet in length.
Such a lengthy neck was beneficial for surprise attacks on fish and squids, allowing it to approach without moving its body.
Thalassomedon’s four flippers, each nearly 7 feet long, enabled it to glide smoothly through the depths.
Temnodontosaurus
Part of the ichthyosaur group, Temnodontosaurus swam the oceans in the Early Jurassic, approximately 200 to 175 million years ago, with fossils mainly located in Europe.

This marine predator, growing up to 30 feet, boasted large eyes, suggesting it might have hunted in deep, dim waters.
Its teeth, sharp and conical, were perfect for gripping slippery prey such as fish and squid.
The Temnodontosaurus’s streamlined body allowed it to dart swiftly through the waters.
Conclusion
The oceans once had amazing marine reptiles that swam alongside fishes. While they weren’t true dinosaurs, they were just as impressive.
From speedy Ichthyosaurs to massive Mosasaurs, these creatures tell us a lot about life in ancient seas. Studying them helps us understand our planet’s history and the incredible variety of life that once existed here.
References
- https://www.snexplores.org/article/real-sea-monsters
- https://www.blueplanetaquarium.com/education/dinosaurs-of-the-sea-ocean-life-in-the-prehistoric-era/
- https://oceanconservancy.org/blog/2021/12/07/prehistoric-animals-ocean/
- https://a-z-animals.com/blog/the-largest-sea-dinosaur-in-history/
Hi, I am Roy Ford a General Studies and English Teacher who has taught all over the world. What started as a fossil collection became a great way to teach, motivate and inspire students of all ages and all over the world about dinosaurs and from that and children’s love of dinosaurs came the site dinosaur facts for kids, a resource for all ages.






